Multiplication of Algebraic Expressions
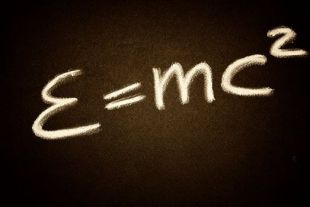
Einstein's famous equation involves multiplying algebraic terms
When we multiply algebraic expressions, we need to remember the Index Laws from the Numbers chapter.
Let's see how algebra multiplication works with a series of examples.
Example 1
Multiply x3(x4 + 5a)
We expand this out using the distributive law:
x3(x4 + 5a)We cannot simplify this answer any further. We present our answer in alphabetical order since it makes it easier to read when the problems become more involved.
= x7 + 5ax3
Example 2
Multiply (x + 5)(a − 6)
We multiply this out as follows. We take each term of the first bracket and multiply them by the second bracket. Then we expand out the result.
(x + 5)(a − 6)We cannot do any more with this answer. There are no like terms, so we cannot simplify it in any way.
= x(a − 6) + 5(a − 6)
=ax − 6x + 5a − 30
Example 3
Multiply (2x + 3)(x2 − x − 5)
We take the 2 terms of the first bracket and multiply both of them by the second bracket.
(2x + 3)(x2− x − 5)
= (2x)(x2 − x − 5) + (3)(x2 − x − 5)
This time we could collect together some like terms. There was:
(2x + 3)(x2− x − 5)
= (2x)(x2 − x − 5) + (3)(x2 − x − 5)
= (2x3 − 2x2 − 10x) + (3x2 − 3x − 15)
= 2x3 + x2 − 13x − 15This time we could collect together some like terms. There was:
−2x2 + 3x2 = x2and
−10x − 3x = −13x
No comments:
Post a Comment